|
|
|||||
Accueil > Actualités > L'Actu des membres et partenaires >CERFACS
2-6 October 2017 - NUMERICAL METHODS FOR LARGE EDDY SIMULATION This training session allows participants to understand the underlying basics of Large Eddy Simulation (LES): numerics, boundary conditions, LES closures and combustion modeling. The CFD code AVBP...... Detailed program. 9-11 October 2017 - CODE COUPLING USING OPENPALM Detailed program. 13 October 2017 - MODAL ANALYSIS OF THERMOACOUSTIC INSTABILITIES USING THE AVSP SOLVER Detailed program. 19 October 2017 - VERSIONING SYSTEMS: INTRODUCTION TO GIT Detailed program. 20 October 2017 - MESH GENERATION USING CENTAUR Detailed program. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
5-9 Oct. 2015 - Numerical methods for Large Eddy Simulation This training session allows participants to understand the underlying basics of Large Eddy Simulation (LES): numerics, boundary conditions, LES closures and combustion modeling. The CFD code AVBP (version 6.2) co-developed by CERFACS and IFPEN is used for hands-on to compute both academic and realistic configurations of reacting compressible flows. 12-14 Oct. 2015 Saclay, France - openpalm-meso : Formation MdS - Cerfacs - Equip@Meso : Couplage de codes avec OpenPALM The OpenPALM coupler co-developed by ONERA and CERFACS has many features, and its use requires a dedicated training for physicists, computer scientists and developers of coupled applications. The purpose of the course is to learn to use PrePALM, the GUI of OpenPALM in order to quickly become autonomous on the instrumentation of the codes to couple as well as to use the various features of the coupler. The course is intended to be pragmatic with many hands-on activities. CERFACS engineers involved in its development teach this course. 15 Oct. 2015 - Versioning systems: introduction to GIT GIT is a distributed revision control and source code management system. It was initially designed for Linux kernel development and is particularly adapted to multi-site and multi-developer environments. In the morning, the basic knowledge of source code managements are taught, presenting most GIT functionalities with many illustrations. A brief comparison with other management tools (Mercurial, CVS, SVN) is also proposed. In the afternoon, a hands-on session with detailed exercices is organized to illustrate the main concepts. 16 Oct. 2015 - Mesh generation using CENTAUR Computational Fluid Dynamics in realistic geometries requires somplex meshes. This training course deals with the basics of unstructured and hybrid meshing using the Centaursoft software. 19 Oct. 2015 - Modal analysis of thermoacoustic instabilities using the AVSP solver This training session aims at learning the participants the basics of combustion instabilities as well as how to use the thermoacoustic code AVSP developed at CERFACS. The latter is a general purpose Helmholtz solver which computes the frequency of oscillation, growth rate and spatial structure of the thermoacoutic modes of interest. Several test cases are considered during this one day training session in order to get the participants acquainted with the different features of AVSP (speed of sound inhomogeneities, complex valued boundary impedance, multi-perforated liners, acoustic flame coupling, multi-burner annular combustors,...). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Data assimilation has become an important component of modelling for a growing number of applications in the geosciences and in engineering. This training course will provide an overview of the theory and practical methods of data assimilation. First the basic concepts from statistical estimation theory and nonlinear optimization will be given. The classical variational and Kalman filtering approaches to data assimilation will then be described. The lectures will also cover more specialized topics including covariance modelling and estimation, advanced minimization algorithms, preconditioning, and hybrid ensemble-variational methods. The lectures on the theory will be complemented by both practical exercises and presentations on specific applications at Cerfacs in the geosciences (oceanography, atmospheric chemistry and hydrology/hydraulics). Detailed program:
There is a strong need in high resolution climate scenarios in France. Given that global climate models produce data at horizontal resolutions ranging from 100 to 200 km, their data output is not suitable for direct use in climate change impact studies at the regional and local scales. Hence, methodologies have been developed to downscale the output of large-scale climate models, such as dynamical or statistical methodologies. One such method has been developed at Cerfacs, the open-source software DSCLIM, a methodology that uses large-scale circulation information from global climate models, and links it to local-scale climate variables using a weather-typing based statistical model. Also, within the FP7 European project SPECS, an open-source R-based downscaling package is being developed. This training course aims to provide scientific and technical knowledge about downscaling methodologies, with hands-on t raining on DSCLIM output analysis. Detailed program:
In this training course, the architectures of today's supercomputers are described. The processor evolution as well as the main types of architectures are then presented. Finally, the methods and tools for code optimization on these supercomputers are described. Detailed program:
GIT is a distributed revision control and source code management system. It was initially designed for Linux kernel development and is particularly adapted to multi-site and multi-developer environments. In the morning, the basic knowledge of source code management are taught, presenting most GIT functionalities with many illustrations. A brief comparison with other management tools (Mercurial, CVS, SVN) is also proposed. In the afternoon, a hands-on session with detailed exercises is organized to illustrate the main concepts. Detailed program:
Computational Fluid Dynamics in realistic geometrics requires complex meshes. This training course deals with the basics of unstructured and hybrid meshing using the CENTAUR software. Detailed program:
This training session allows participants to understand the underlying basics of Large Eddy Simulation (LES): numerics, boundary conditions, LES closures and combustion modeling. The CFD code AVBP (new version V7.0) co-developed by Cerfacs and IFPEN is used for hands-on to compute both academic and realistic configurations of reacting compressible flows. Detailed program:
CERFACS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
1er septembre 2014 -
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
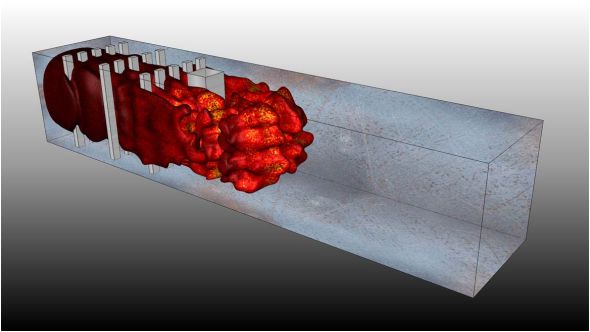
20 janvier 2014 - Le programme INCITE vient d'annoncer que le CERFACS avait reçu une nouvelle allocation de 86 millions d'heures pour 2014 pour calculer la propagation de flammes turbulentes dans des batiments lors d'explosions accidentelles. Grâce au support de TOTAL, le CERFACS dispose aujourd'hui d'une base de données expérimentale unique sur ces thèmes puisque trois expérimentations exactement similaires en géométrie mais à des échelles 1, 6 et 24 ont été réalisées en Australie et en Norvége. Ces résultats expérimentaux combinés à la puissance de calcul disponible sur la machine INCITE (un BG/Q IBM) vont permettre de tester les modèles sur une gamme de paramètres jamais testée jusqu'ici. Le CERFACS est un des très rares groupes de recherche au monde ayant des allocations de temps CPU à la fois dans PRACE et INCITE.
Simulation aux grandes échelles d'une explosion dans un bâtiment (calcul INCITE) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16/12/2011 - destinées aux étudiants, doctorants, ingénieurs et chercheurs, des secteurs académiques et appliqués.
Les formations sont données par les chercheurs et ingénieurs du CERFACS, et sont soit généralistes dans le domaine du calcul et des mathématiques appliquées, soit spécifiques aux domaines d'expertise du CERFACS. Des formations pratiques aux logiciels développés ou co-développés par le CERFACS (AVBP, OpenPALM, DSCLIM, CESC, OASIS) sont incluses dans ce programme. Elles sont organisées au CERFACS qui est agréé pour dispenser des formations éligibles au Droit Individuel à la Formation (DIF). Les 3 prochaines formations au CERFACS Couplage de codes avec OpenPALM. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 08/02/2011 - Formation de base au coupleur Open-PALM La prochaine formation de base au coupleur Open-PALM se déroulera au CERFACS à Toulouse du lundi 18 au mercredi 20 avril 2011. Les cours se présentent sous forme de travaux pratiques pour apprendre à maitriser l'interface graphique PrePALM et aborder les différentes fonctionnalités du coupleur : couplage dynamique, gestion de processus, couplage parallèle, communications, redistribution de données, interpolation temporelle, etc. Vous trouverez une description détaillée du coupleur et des exemples d'utilisation sur le site web d'Open-PALM: www.cerfacs.fr Le coût de la formation est de 800 euros HT pour les trois jours, moitié prix (400 euros) pour les agents CNRS. La formation est gratuite pour les partenaires du CERFACS, soit : METEO-FRANCE, ONERA, SAFRAN (SNECMA et TURBOMECA), EDF, CNES, EADS et TOTAL.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||